Open & Extensible
Low-Code Development
Go beyond the low-code status quo with the interoperable Mendix platform
Try Mendix for FreeTrusted by
Develop applications without limits
The Mendix low-code application development platform is built on open standards and open-source technologies, giving developers unlimited opportunities to extend platform and application capabilities.
Seamlessly integrate the platform with your tech stack, extend applications with custom code, leverage open APIs to programmatically adjust models, and build beyond the standard expectations of low-code. Mendix is open and extensible at every level.
Get startedPlatform extensibility
Adapt the Mendix platform to your enterprise development needs
-
![]()
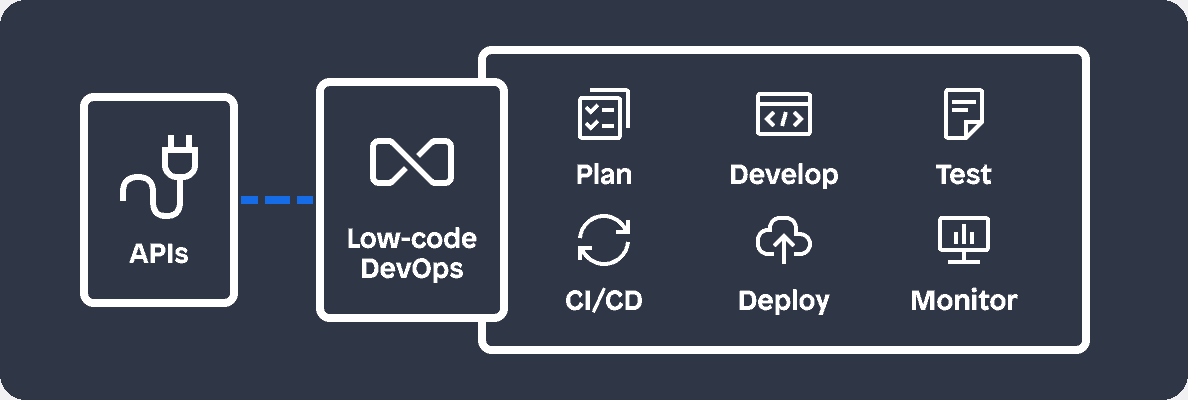
Platform
The core functionality of the Mendix platform is accessible through APIs. Developers can connect Mendix with existing technologies, incorporate third-party testing services, or use automation services (such as Jenkins or GitLab) to orchestrate a CI/CD pipeline.
- Integrate Mendix with third-party systems and applications
- Connect Mendix to your existing CI/CD pipeline
- Create application projects
- Manage sprints, stories, user feedback, permissions, and security
- Automate the migration of applications to other platforms with the Mendix Platform SDK
-
![]()
Models
With the Mendix Model SDK, developers can access the core of every Mendix application, including: microflows, custom widgets, security constraints, Java actions, and more. We ensure these models are fully open, accessible, and shareable.
- Migrate legacy applications to the cloud
- Read, modify, and analyze the model of any application
- Choose how you migrate applications to and from Mendix
"When integrations are required, Mendix is preferred."
Application extensibility
Extend the capabilities of your applications with reusable components and custom code
-
Front-end
Developers can extend the front-end capabilities of every application using custom-built widgets and actions leveraging Javascript. Mendix empowers developers to use open frameworks like React Native, PWA, and Mendix’s Atlas UI to build engaging web and mobile application experiences.
- Leveraging the Mendix Client Javascript library to connect to data, logic, and pages modeled in your Mendix IDE
- Use existing open-sourced libraries with tools such as Node Package Manager (NPM)
- Incorporate third-party React Native components to enhance the UX for native mobile applications
-
Integrations
Integrate Mendix with your ecosystem of third-party software tools and technology with support for REST, SOAP, GraphQL, and JDBC. Developers work more efficiently in Mendix by easily accessing and exposing information in your existing application portfolio.
- Unlock and govern low-code data integration with Mendix Connect
- Easily leverage open standards and third-party services within your Mendix applications
- Expose live Mendix application data in one click for consumption in BI tools like Tableau, analytics platforms like SAS and R, or in Excel with Mendix OData support
-
![]()
Runtime
The Mendix Runtime is implemented using Scala and Java and runs on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), which gives you portability across environments. Developers can use custom Java/Scala code to extend the possibilities of the Mendix Runtime.
- Extend the Platform’s runtime capabilities with Java actions
- Leverage existing Java/Scala libraries in your applications
- Use tools like Maven and Gradle to control your dependencies
-
Cloud
Mendix is cloud-native by default, and applications are containerized, portable, and resilient out of the box. With our multi-cloud capabilities, developers have the freedom to deploys applications on their own terms, backed by the support of our high availability, robust security, and unmatched reliability.
- Deploy applications to your chosen architecture in just one click
- Use our multi-cloud capabilities to manage applications in Mendix Cloud, Mendix Cloud Dedicated, Mendix for Private Cloud, or on-premise
- Deliver solutions faster with our industry best 99.95% enterprise uptime guarantee*
*For premium versions
"Mendix offers quite a few modules and tools to integrate with SAP very easily using the SAP OData Connector, SAP BAPI Connector, and the SAP Data Model Connector...And on the deployment side it's one-click deployment...It's just a matter of creating a package and clicking a single button — seamlessly integrated."
FAQs
-
What is the difference between an open and closed platform?
An open application development platform provides accessible APIs and enables developers to connect with third-party systems. All open-source platforms are considered open, but not all open platforms are open-source.
A closed platform can be customized, but only by developers with proprietary knowledge and capabilities. Closed platforms have more restrictions, including difficulty integrating with third-party tools.
-
How can the extensibility of a platform benefit a business?
Open and extensible application development platforms are beneficial for every enterprise. By extending a low-code platform to fit business and development needs, enterprises are able to adapt and respond swiftly to disruptions and changing requirements.
Developers are empowered to build new functionalities, extend capabilities, and integrate with third-party tools, opening up a limitless world of possibilities for your organization.
More resources
-
![Sync vs Async]()
Explained: Asynchronous vs. Synchronous Programming
Asynchronous vs. synchronous programming: What are the similarities and differences? Learn about these two distinct approaches here.
-
![Programming in a Low-Code World]()
Programming in a Low-Code World
Learn how software engineers and programmers can thrive with low-code in a model-driven development platform.
-
![enterprise application architecture]()
Enterprise Application Architecture: Best Practices & Strategies
Discover the different styles of enterprise application architecture and how they impact software design and development.
-
![fusion team]()
Fusion Teams, Explained: Benefits, Roles & Examples
What are fusion teams and how do they accelerate application development? See examples, challenges, benefits, and more in this fusion team deep dive.
-
![]()
Accelerate Business Impact with the Mendix Ecosystem
Discover how the Mendix platform ecosystem can help enterprises succeed in today's volatile economy.
-
![Title Image]()
Software Composition: Why, What, and How
Dive into Software Composition, a newly released capability that provides an accurate inventory of application and application landscape component dependencies.