Accelerate to a New Realm of Lean Manufacturing with Mendix
In the current context of global economic downturn, enterprises face unprecedented challenges. To remain competitive in such an environment, companies must seek effective management strategies to improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance competitiveness.
Lean management, as a management model aimed at reducing waste, improving efficiency, and ensuring quality, has become an important means for companies to address the challenges of economic downturns. The core idea is to eliminate all kinds of waste in the business operation process, including waste of time, resources, and labor, to achieve process optimization and efficiency improvements. Lean management not only focuses on the production process but also extends to the entire value chain, including supply chain management, quality management, human resource management, and more.
Lack of lean management can impact various aspects of business operations:
- Enterprises may fail to accurately assess resource requirements during the production process, leading to over-investment or uneven allocation of resources such as manpower, materials, and finances.
- Lean management emphasizes quality control and continuous improvement. Without these mechanisms, product quality may become unstable, resulting in increased defects and rework, which not only raises costs but also damages the company’s reputation and customer satisfaction.
- In an increasingly competitive market, companies lacking lean management may struggle to compete with rivals.
- Lean management helps enterprises achieve cost control and maximize profitability. A lack of lean management could lead to poor cost control and deteriorating financial health.
- Lean management emphasizes teamwork, continuous improvement, and a culture of excellence. Companies without lean management may lack this positive cultural atmosphere, leading to low employee morale and poor team collaboration.
Challenges in Implementing Lean Manufacturing
The concept of lean manufacturing holds tremendous strategic significance and business value for manufacturing enterprises. However, its implementation often faces numerous practical challenges:
- Traditional thinking constraints. Long-standing traditional production concepts in manufacturing enterprises are deeply rooted, such as focusing more on quantity and speed in mass production models. In contrast, lean production emphasizes eliminating waste, optimizing processes, and continuous improvement. Employees may find it difficult to quickly embrace new concepts. Misunderstandings about lean production are also common. Some managers view it merely as a set of tools or methods, ignoring its systemic and holistic nature, which leads to suboptimal implementation.
- Systematic planning is required to implement lean production, including setting goals, analyzing processes, and formulating improvement measures. A lack of systematic planning may result in a chaotic implementation process with unclear outcomes. Integrating lean production into an already mature management system requires coordination among various parties and process adjustments, potentially leading to departmental conflicts and coordination difficulties.
- Lack of professional talent. Lean production requires professionals with knowledge and skills, including lean experts, project managers, and frontline employees. A shortage of such professionals may hinder progress and quality. Employee training can also be challenging. Employees need to understand lean production concepts, methods, and tools, requiring substantial training and practice. However, busy schedules or ineffective training may hinder their ability to quickly acquire the necessary knowledge and skills.
- Conflict between short-term benefits and long-term goals. The benefits of lean production often take time to materialize. During the initial stages of implementation, it may increase employees’ workloads without immediately demonstrating tangible benefits, resulting in low enthusiasm and difficulties in sustaining efforts.
- Lack of effective incentive mechanisms. Without effective incentives to encourage employees to actively participate in lean production improvements, they may lack motivation, making continuous improvement difficult to achieve.
- Internal departmental coordination issues. Lean production requires active cooperation from multiple departments, such as finance, HR, and procurement. Differences in responsibilities and goals may lead to disputes and inefficiencies, impacting the overall outcome. Low supplier cooperation levels can also be a challenge. Lean production demands high-quality, timely materials and components. Suppliers’ inability to meet these requirements may disrupt production schedules and affect product quality, hindering the implementation of lean production.
Mendix Low-Code Supporting Lean Manufacturing
Finding practical and context-appropriate methods is crucial for advancing lean manufacturing in enterprises. Collaboration between business and IT, long-term planning with agile delivery, personnel transformation, and capability reuse are essential competencies for addressing lean manufacturing challenges. Siemens’ Mendix low-code platform is undoubtedly a handy “tool.”
As a low-code platform under Siemens, Mendix plays a critical role in the digitalization process. Renowned for its efficient development capabilities, Mendix facilitates the rapid creation of digital applications through graphical and modular programming, shortening development cycles and seizing market opportunities. Moreover, Mendix breaks technical barriers with its visual and graphical interface, enabling non-IT personnel to participate in development after simple training, fostering collaboration between business and IT and ensuring applications meet business needs. The platform also offers pre-built components, templates, automated testing, and deployment functionalities to enhance development efficiency and quality, meeting changing business requirements.
Volkswagen Anhui Co., Ltd. leveraged the Mendix low-code platform with support from the company’s IT&D department, enabling the business team to achieve digital innovation in the shortest possible time. By integrating digitalization with lean and continuous improvement concepts, the company consistently improved operational efficiency and reduced management costs.
Within three months of formally adopting the Mendix low-code platform, the company had 4 applications in the deployment phase, with related work efficiency improved by 20% – 40%. Liu Yaozhong, Head of Intelligent Efficiency Department, remarked: With the help of low-code tools, colleagues in front-line business departments now have tools to implement digital lean improvements. The factory’s digital transformation can not only rely on large-scale, long-term, high-investment projects but also benefit from gradual, short-term, low-investment continuous improvement initiatives. (view the detailed case study of Volkswagen Anhui)
BMW Brilliance combined lean methodology with Mendix to quickly build 15 applications. For example, the VMI (Vendor Management Inventory) application has enabled zero inventory management for over 10,000 materials, effectively reducing inventory levels by more than 50 million in the future and significantly saving material procurement budgets and inventory management costs.
Senior Logistics Project Advisor Gao Xianfu stated: The company has always been committed to lean production. Today, digitalization has become the most effective means of implementing lean concepts, and the Mendix low-code platform, with its efficiency and flexibility, accelerates the lean digitalization process. It simplifies the development process, allowing non-technical personnel to quickly get started, fostering deeper integration of business and technology. Through rapid iteration and deployment, it precisely meets market demands, helping the company optimize operations, enhance competitiveness, and achieve lean digital transformation. (view BMW Brilliance’s detailed sharing)
Building Fusion Teams for “Roundtable Development”
To accelerate digitalization, Mendix has also established fusion teams. The concept of Fusion Teams, proposed by Gartner, emphasizes tightly integrating the deep technical expertise of professional developers with the extensive domain knowledge of business experts to form a unified elite team, driving both collaboration efficiency and business output.
Mendix fusion teams are composed of members with diverse digital skills, disciplines, and expertise. By breaking down departmental silos and combining technical, analytical, and domain knowledge, fusion teams are outcome-focused on business and customer success, accelerating application development and deployment.
To meet the varied needs of team members—such as business personnel, IT experts, analysts, designers, developers, and data teams—Mendix offers cross-functional collaboration tools that support the entire project lifecycle. The platform also provides specialized modules for portfolio management, project management, control centers, and application feedback management, enabling team members to collaborate efficiently within their areas of expertise.
In the modeling and development stage, Mendix leverages its product features and extensive practical experience to propose a right-shifting model for low-code development that combines business and IT co-development. This methodology encompasses initial capability assessment, complexity quantification, continuous enablement, capability certification, and enterprise low-code asset management. Over time, this enables business teams to undertake more application development under IT’s guidance, responding rapidly to business needs. This model has been successfully implemented by many clients, significantly enhancing development efficiency. Some clients have even referred to it as “roundtable development.”
In summary, with low-code and fusion teams, Mendix provides both technical and talent assurances for enterprise digitalization, facilitating digital transformation and enabling lean manufacturing.
Mendix Accelerates Siemens’ First Fully Integrated Native Digital Factory
In the construction of new factories within Siemens Group, Mendix low-code has played a pivotal role in driving lean manufacturing. In 2022, the Siemens Numerical Control (Nanjing) Co., Ltd. (SNC) new factory was commissioned. This is Siemens’ first fully integrated native digital factory globally, showcasing Siemens’ digital native technologies throughout its design, planning, and operational management, including the use of Mendix low-code.
From the perspective of the new factory, Mendix low-code significantly lowers the technical barrier with its graphical and modular programming methods, enabling business personnel without an IT background to actively participate in projects, jointly promoting the rapid development of digital factories. Furthermore, Mendix aligns closely with Siemens’ development strategies.
It supports multi-platform development, meeting Siemens’ expanding digitalization needs. Additionally, it integrates seamlessly with SNC’s core systems, offering rich interface configurations and robust compatibility. Mendix also excels in front-end and back-end integration, providing strong support for agile development.
Notably, Mendix low-code technology comes with a self-built Mendix technical community and free online expert support, forming a robust technical ecosystem. This allows Siemens to efficiently train employees for its digitalization initiatives. The digital transformation journey becomes similar to a hero’s quest, where even seemingly insurmountable challenges are met with timely expert assistance.
After adopting the Mendix low-code platform, Siemens’ new factory achieved remarkable results. From a talent development perspective, over two years, more than 140 employees joined the Mendix developer community, with 90+ earning professional certifications, and 25 accumulating successful project experience. In terms of deployment, the Nanjing factory successfully implemented and operated 10 applications, including the 3i system, blue-collar scheduling system, and motor production scheduling system. Within 3-4 months, 7 applications were launched, and a repository of over 30 case studies was established, providing valuable resources for future development.
Additionally, participation in digital transformation expanded from a select few to a majority, with the focus shifting from technical to business aspects. This deep integration of core and branch systems enhanced the factory’s confidence in digital transformation at all levels. For non-IT colleagues, Mendix significantly lowered the technical threshold, enabling easier participation in digital transformation and boosting overall engagement and enthusiasm. (watch the Siemens SNC interview video)
In conclusion, digitalization has become an essential path to lean manufacturing. Mendix, with its powerful low-code development platform, helps enterprises quickly achieve digital transformation, enabling business personnel to participate in IT development, reducing gaps, and improving processes and efficiency. Mendix has also introduced a localized Chinese version, better catering to the requirements of Chinese customers for lean practices.

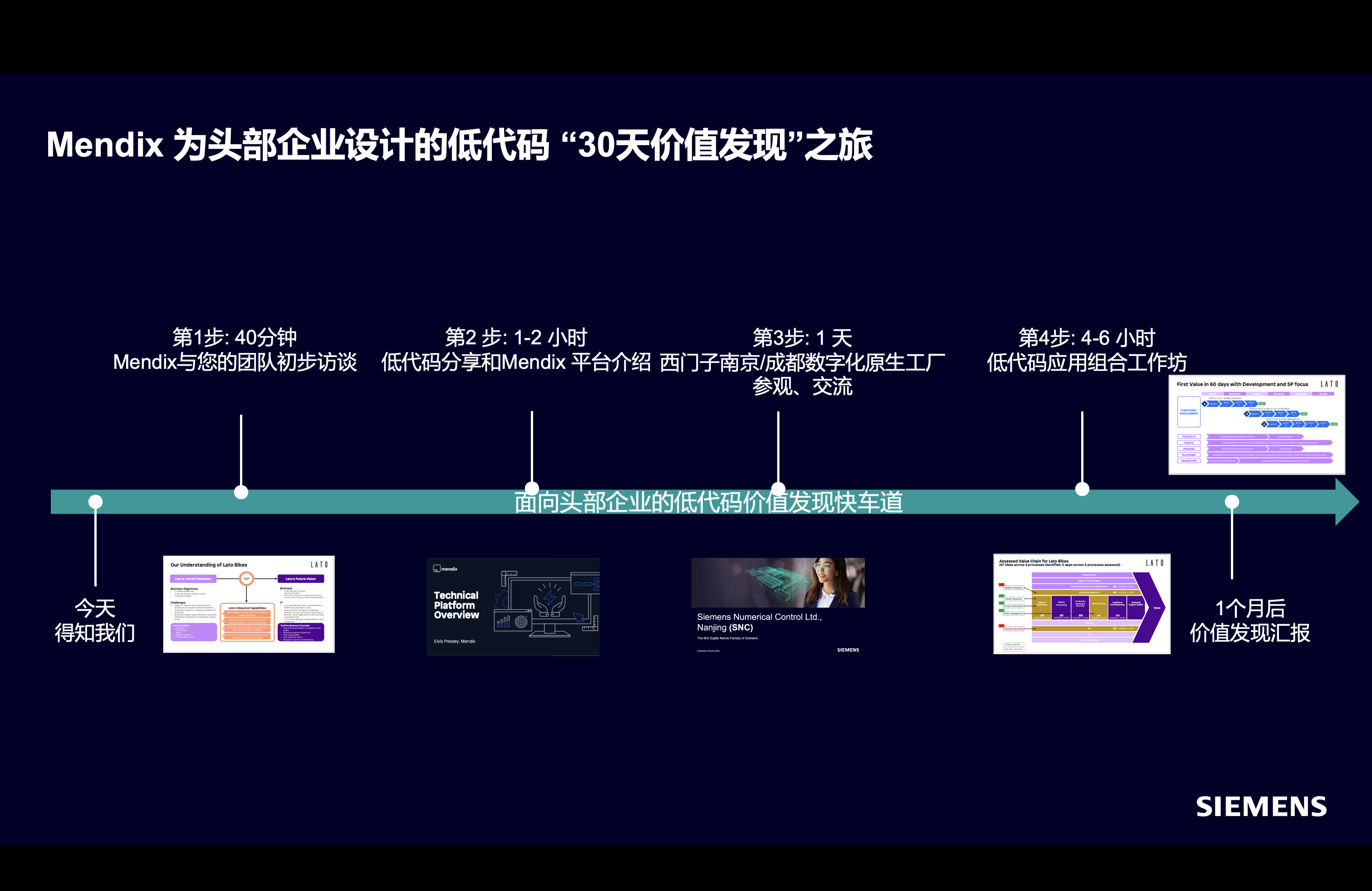
Additionally, Mendix has designed a low-code “30-Day Value Discovery Journey” for leading enterprises. Through this “fast track,” businesses can experience Mendix’s powerful capabilities firsthand and “discover” the immense value it can bring within 30 days, accelerating their digital transformation journey and advancing toward a new realm of lean manufacturing.